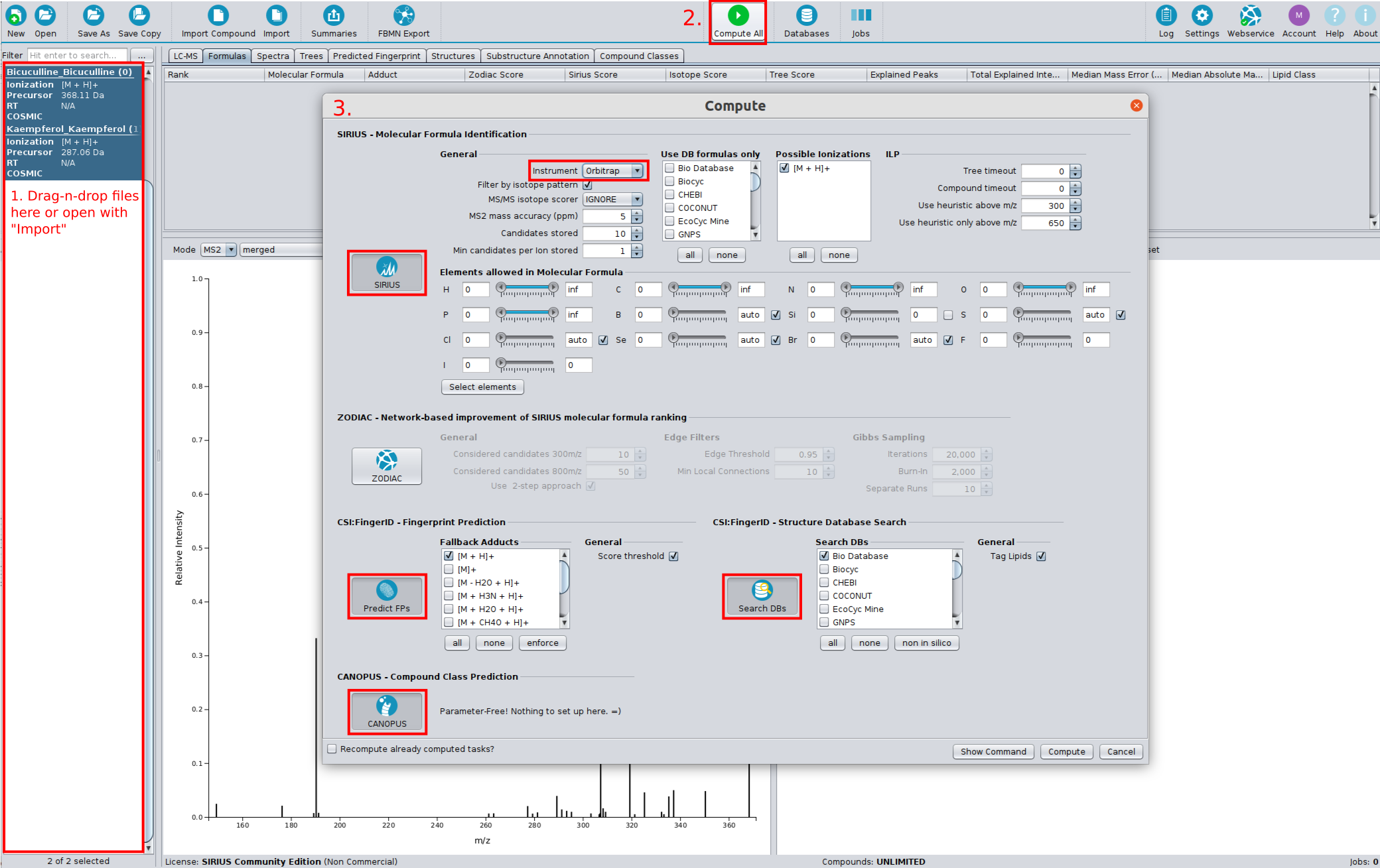
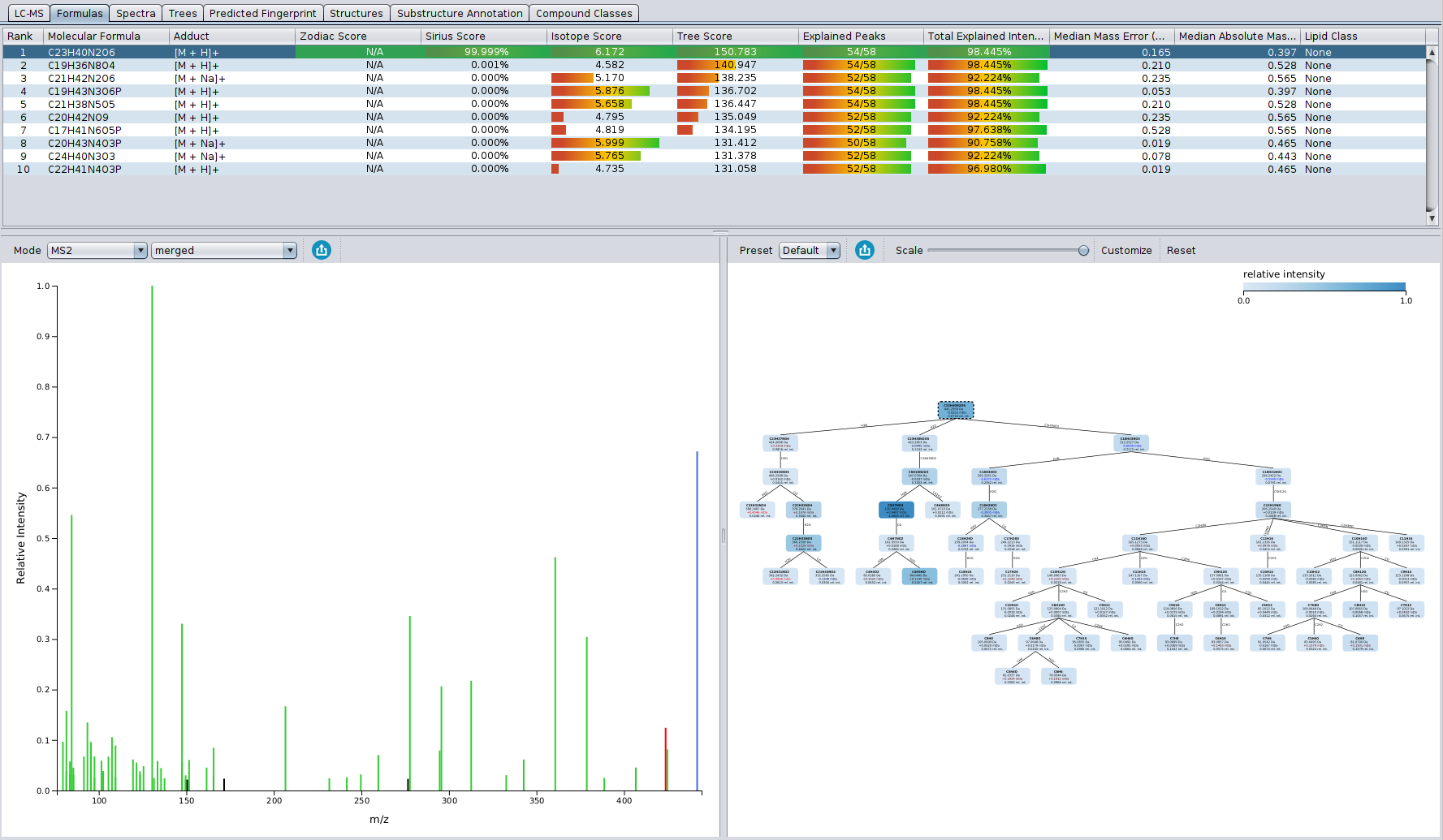
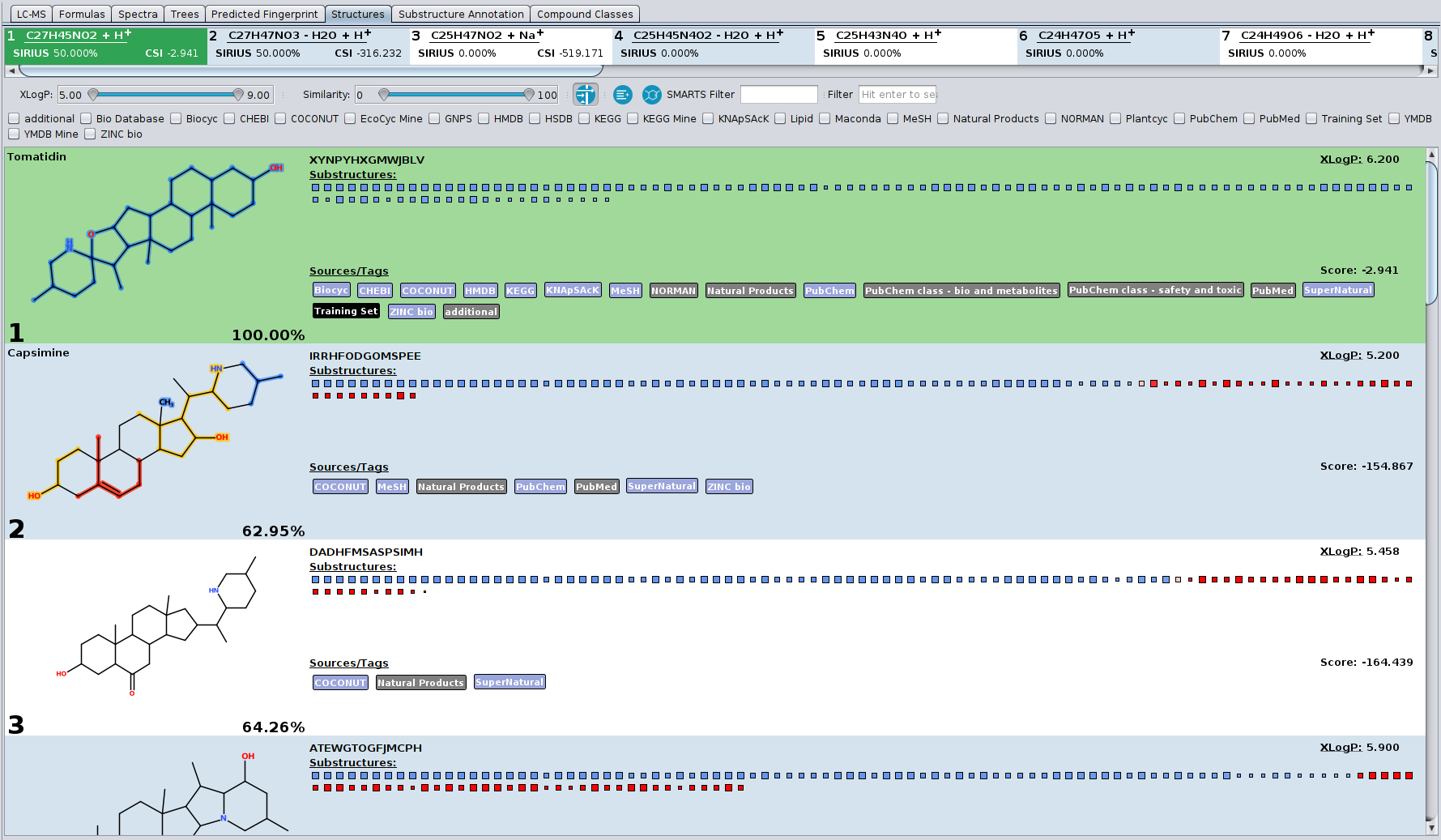
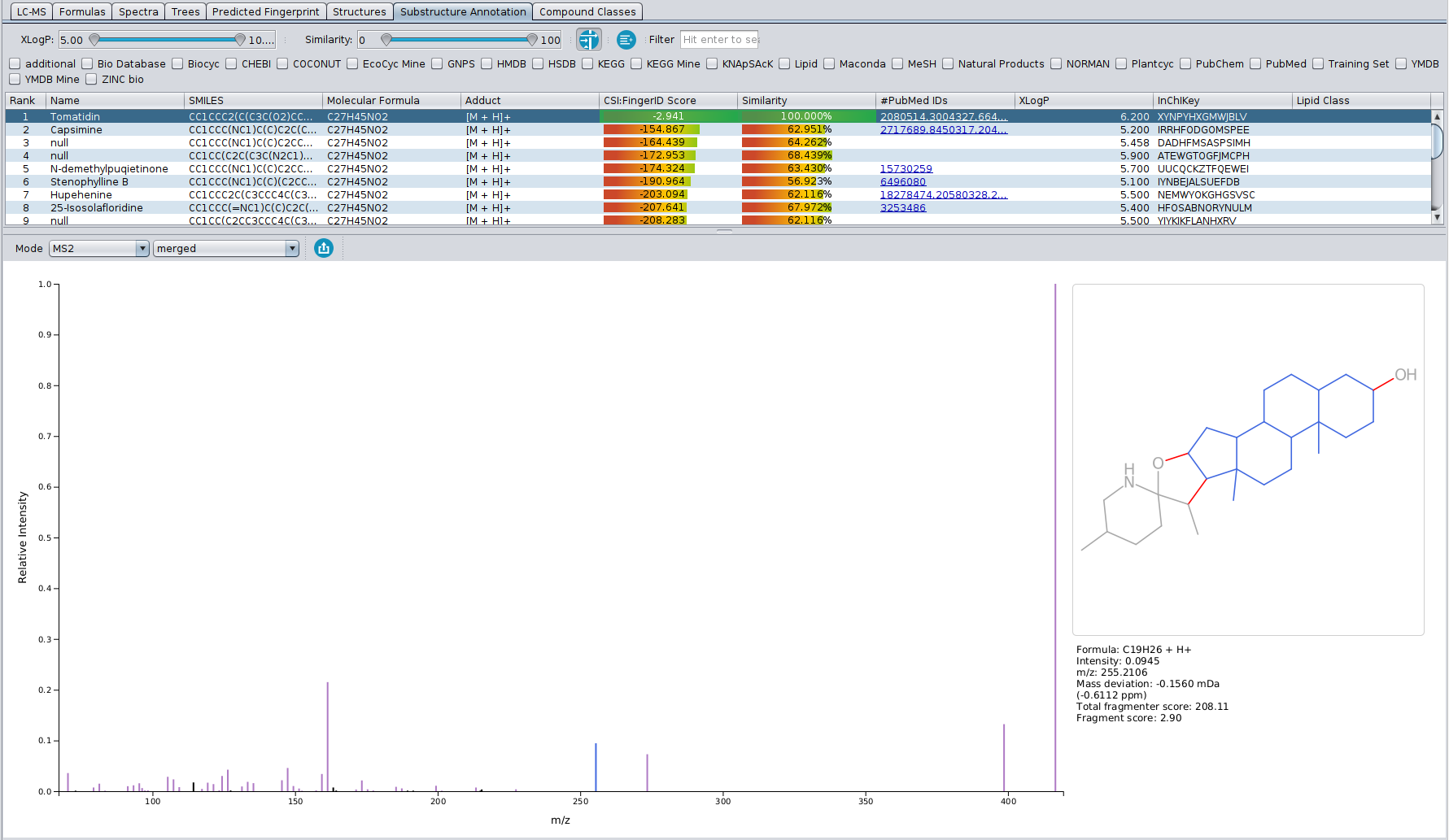
…and why you should also be very careful when doing so
Hi all, I (Sebastian) have recorded a talk about metascores which is now available from our YouTube channel at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mkfG6-ZqD0s. With “metascores”, I mean scores that are not based on the actual data (or metadata!) but rather on side information such as citation counts or production volumes of metabolites. See below for the distinction between metascores and metadata.
I have been thinking about recording such a talk for several years now. I never did, partly because I hoped that this topic would “go away” without me doing such a video. I was wrong, metascores are still in much use today. The other reason not recording the talk was that the more I thought about metascores, the more problems came into my mind. So, I added more slides to the talk, and then I had to re-record the talk, and so on ad infinitum. I now present six problems in the video; I decided I better record it before a seventh problem pops up.
I want to make clear that there is nothing bad with metascores as long as you are using them for a confined application: That is, you want to identify one particular feature in your LC-MS run, and for that you need some candidate compounds to get things started. If this is what you are after, and the actual identification is performed by an independent method (say, buying a commercial standard and doing a spike-in experiment) then you can generate the sorted list of candidates by any method that suits you; that clearly includes metascores. But as soon as you are doing “untargeted metabolomics” or anything similar to that, and as soon as you are using annotations of an in silico method to derive downstream information, you are in trouble — as explained in the video.
I discuss six problems of metascores in the talk, and I thought I will also shortly discuss them here. But first, let us discuss metascores vs. metadata.
Metascores vs. metadata
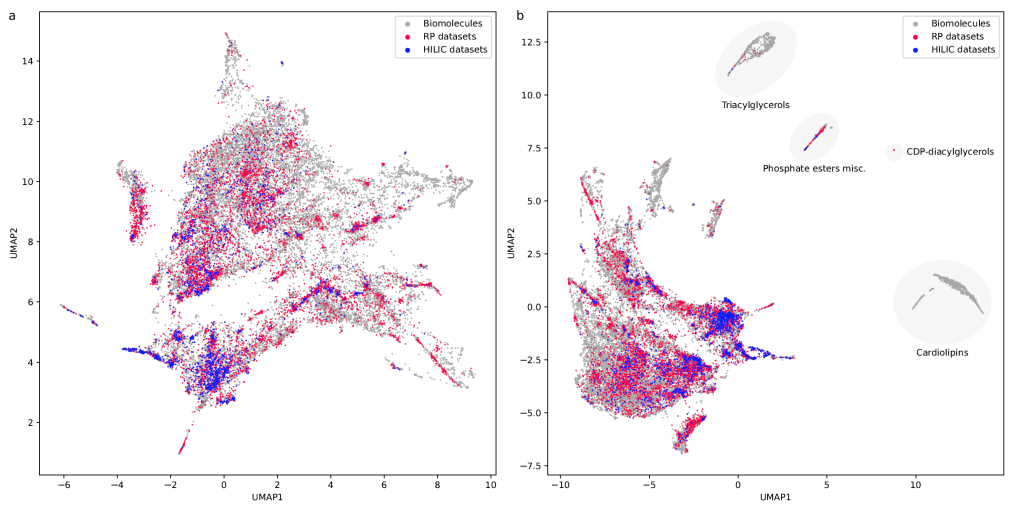
I previously had some discussions about metascores, and I have come to believe that some people think highly of metascores because of the connection to metadata. Well, point is, this is merely a misunderstanding. Metascores and metadata have nothing in common but the prefix “meta”. Metadata is data about your data; it is already used by in silico methods, be it the mass accuracy of the measurement or the ion mode. Metascores — at least the ones I am aware of — use side information, information which has nothing to do with the actual experiment you are conducting. See here for details. Side note: Using such side information (priors) has been discussed repeatedly in other fields such as transcriptomics or proteomics, but has been abandoned everywhere else many years ago.
1st problem: Blockbuster metabolites
This is potentially the biggest single issue of metascores: You will annotate the same metabolites again and again. They are simply “so much cooler” than everything else that a method can basically ignore the data. Who will not love to watch another blockbuster movie? And who will not love to annotate another blockbuster metabolite? See here for details.
2nd problem: Evaluation results are misleading
This is not so much a problem of metascores, but one that is caused by the interplay of metascores and the data we use for evaluations. In short, do not trust evaluations of metascores; the data used for evaluating them are basically from blockbuster metabolites. Which metascores will then correctly annotate, because they love to annotate blockbuster metabolites, and only blockbuster metabolites. See here for details.
3rd problem: Obfuscating good search results
When I say that metascore methods can basically ignore the MS/MS data, this is not as good as it may sound. These methods will obfuscate high-quality search results of an in silico method, and make it impossible for you to decide whether or not a particular search result is worth to follow up on. This issue gets dramatic if you use annotations to generate, say, statistics about the sample. In short: Never do any further analysis on annotations when a metascore was in play. See here for details.
4th problem: Why are you using MS/MS anyways?
It turns out that using a metascore, you can actually forget about MS/MS data; in evaluations, this data are no longer needed to reach good annotation rates. Isn’t that great news: We can do untargeted metabolomics and get away with LC-MS data, saving ourselves the troubles of recording MS/MS data at all! A classical win-win situation: Faster measurements and untargeted metabolomics. Citing Leonard Hofstadter: “Our babies will be smart and beautiful.” See here for details.
5th problem: You are not searching where you think you are
This problem makes me nervous, personally. We are basically saying we are searching throughout the whole planet Earth when in fact, we are searching only in our apartment. I doubt that I can get across the implications of doing so; but this is a horror for reproducibility, method disclosure etc. See here for details.
6th problem: Overfitting
But citations are a reasonable feature for compound annotation, right? And, metascores using citation numbers improve search results, right? Doesn’t that mean something? Short answer: No. We can also reach excellent search results with a metascore that is using moonstruck features such as “number of consonants in the PubChem synonyms”. See here for details.
I also have a few suggestions how I would proceed, instead of using a metascore. I am convinced that these suggestions are not the final word; rather, they are meant as a starting point.
Hope this talk helps to clear the perception of this particular computational method. Best regards, Sebastian.